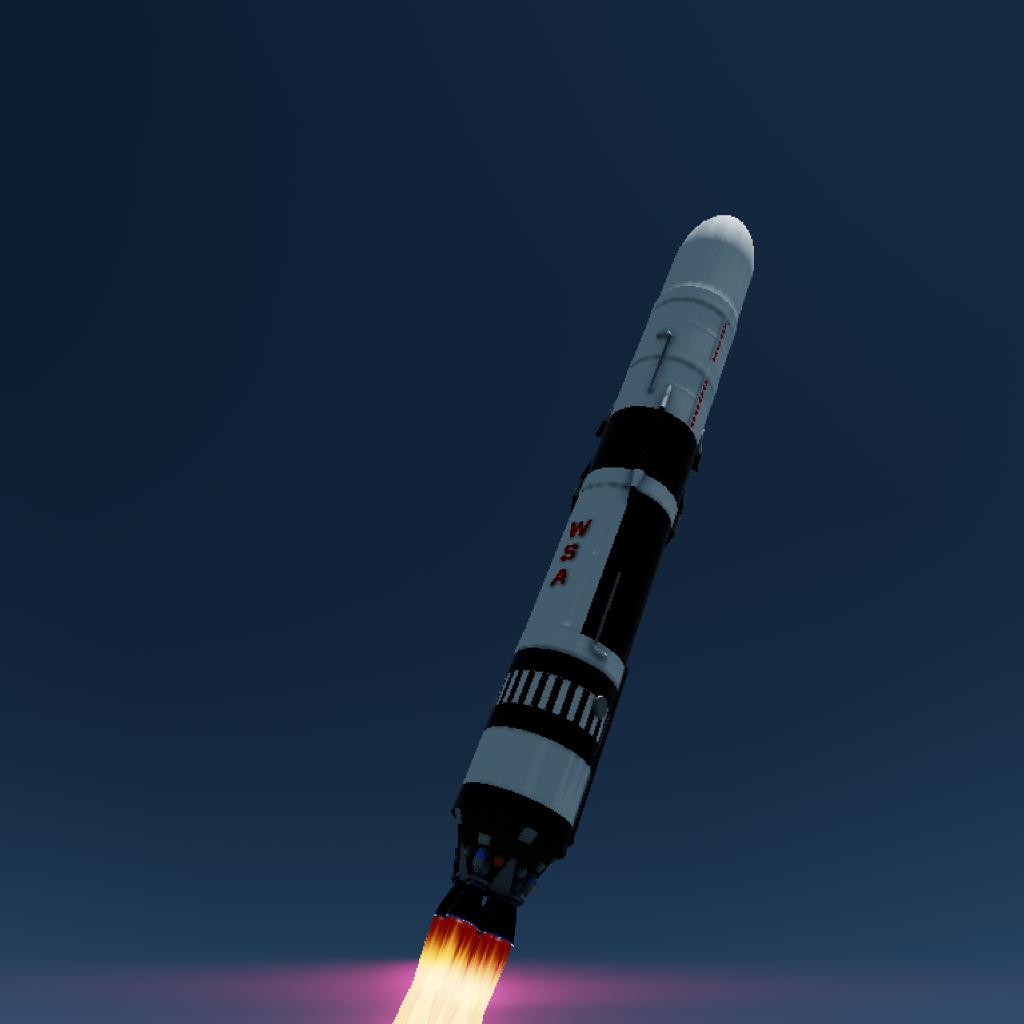
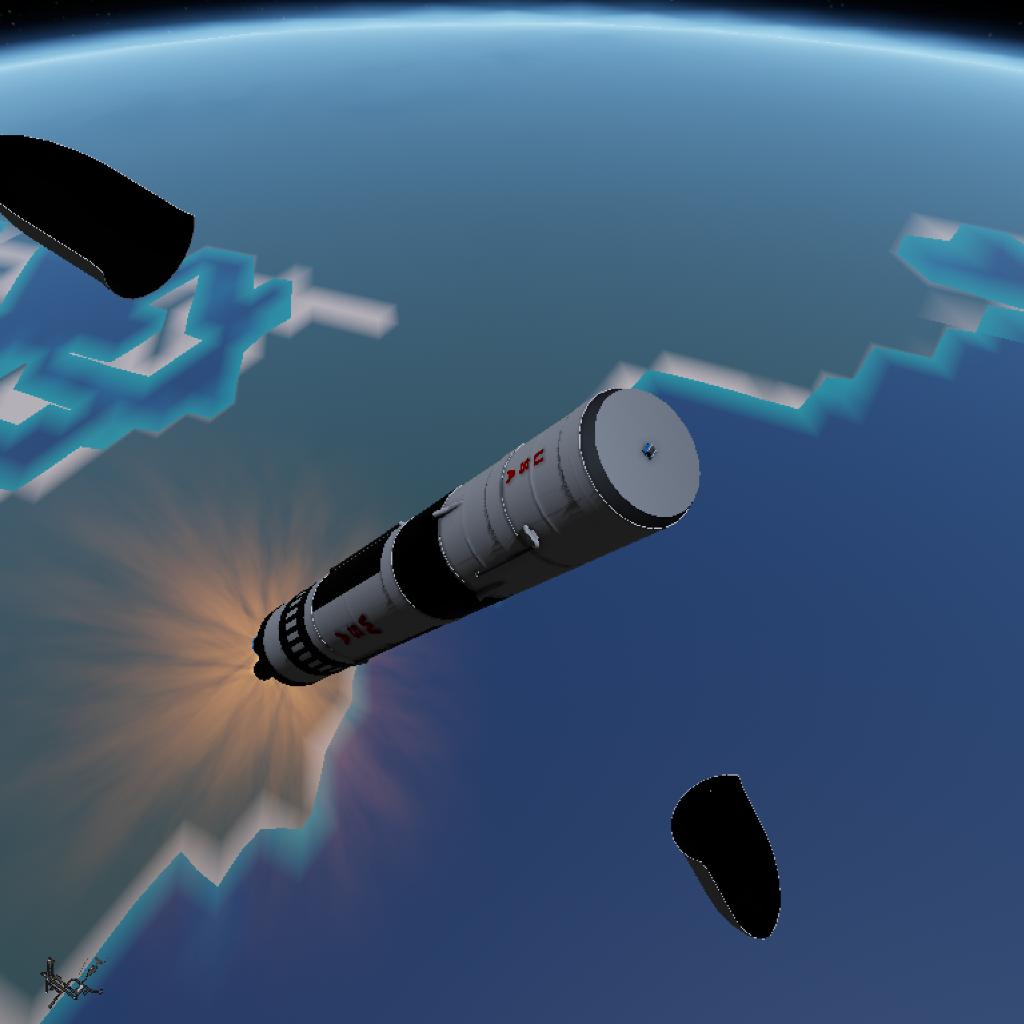
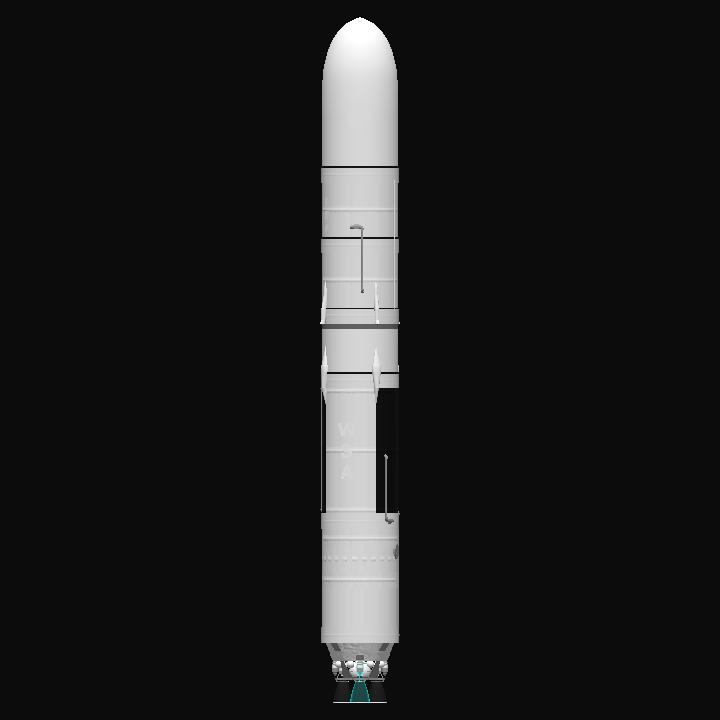
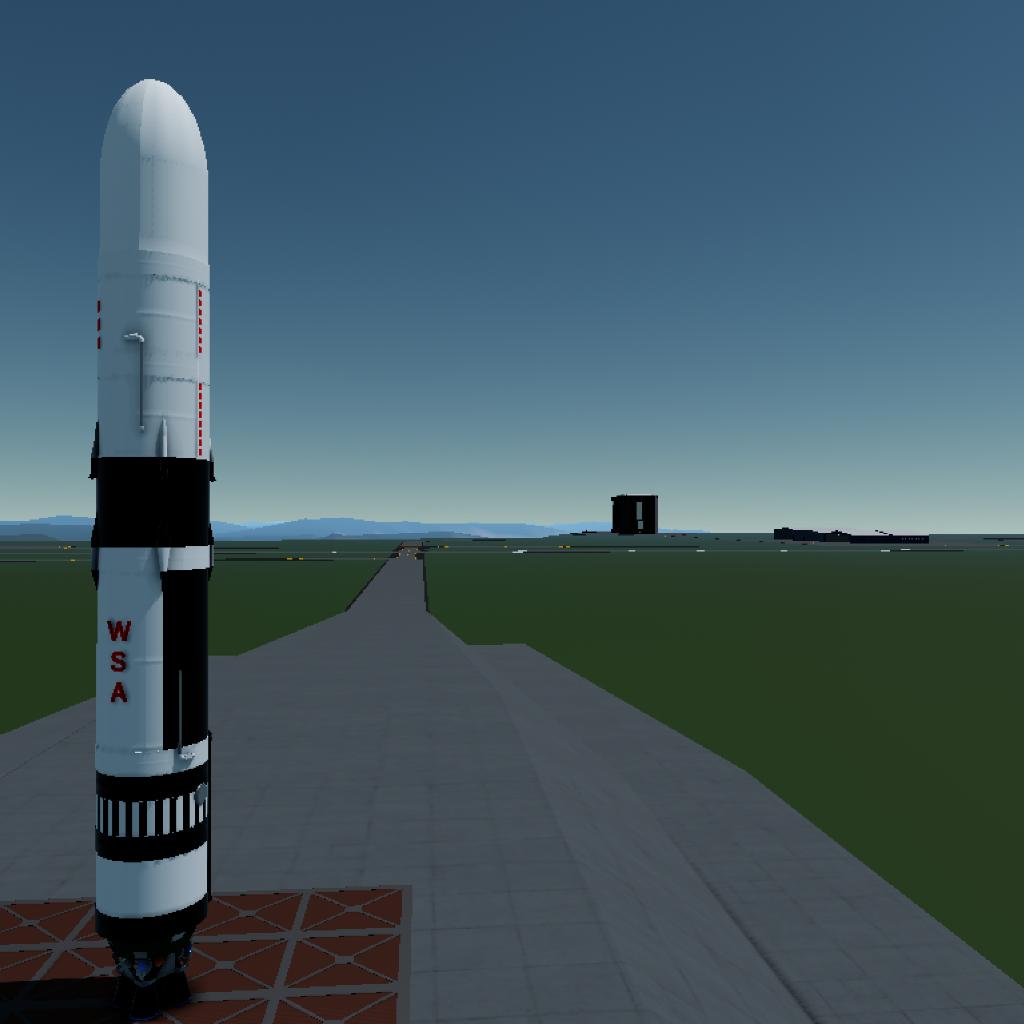
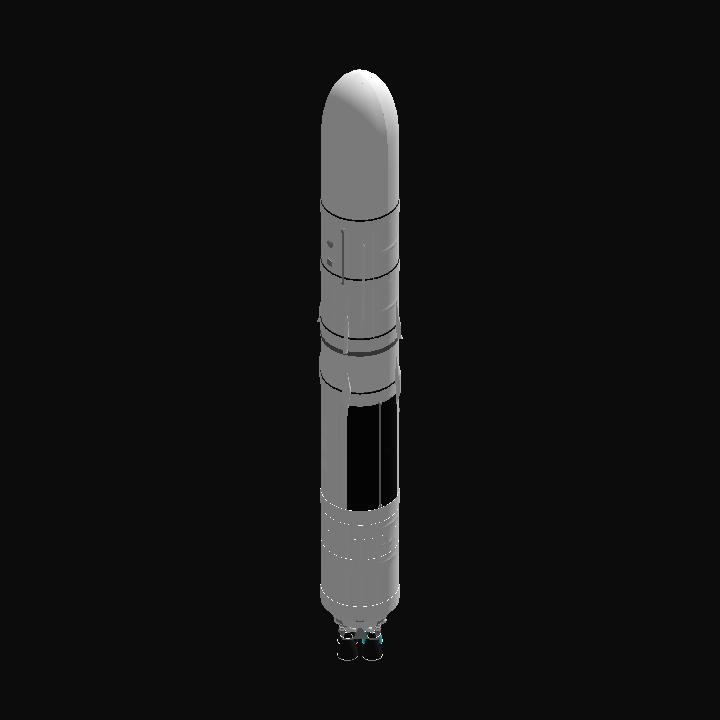
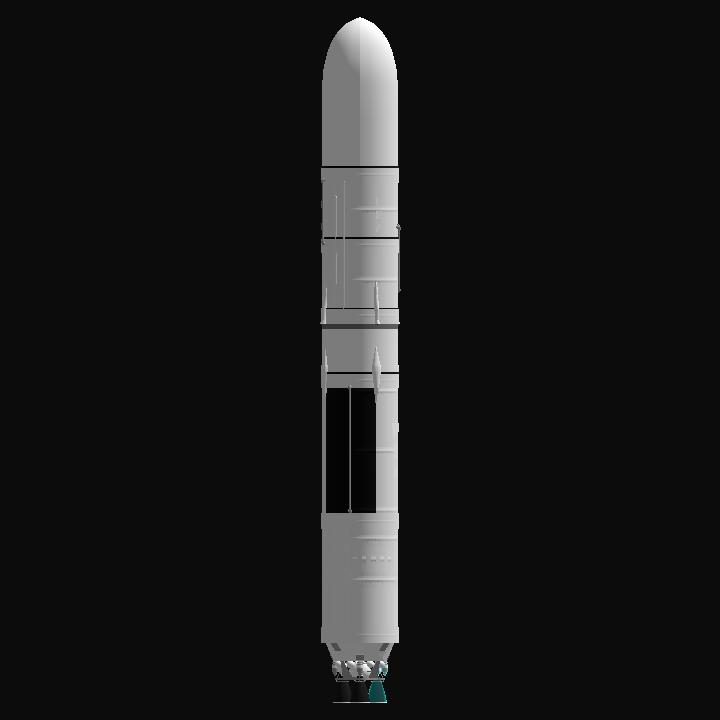
the SIL Project paves the way for a future where the wonders of the universe are ours to explore and behold.
Massive thank you to
@TL0SR2
For helping save me days trying to fix something that was really hard.
summary of the whole desc
This rocket, developed through the SIL Project. features a clustered arrangement of four main liquid rocket engines in its first stage. The second stage employs a single liquid rocket engine fueled by liquid hydrogen and liquid oxygen. This keeps it complex but easy to use. The max payload weight is 120 tons to LEO.
Upcoming Mission Profile:
Mission Name:
"Cosmic Explorer"
Mission Objective:
To deploy the "Celestial Mapper" satellite into a polar sun-synchronous orbit for advanced Earth observation and environmental monitoring.
Satellite Details:
Name: Celestial Mapper
Dimensions:
Length: 3 meters
Width: 2 meters
Height: 2 meters
Weight: Approximately 1,500 kilograms
Payload: Advanced multispectral imaging sensors, atmospheric monitoring instruments, and high-resolution cameras for detailed Earth observation.
Mission Plans
The "Cosmic Explorer" mission is scheduled for launch in the first quarter of May 2025 from WSA's space launch facility.
The "Stellar Vanguard" rocket will carry the "Celestial Mapper" satellite as its primary payload, along with secondary payloads from various international partners.
Following liftoff, the rocket will ascend into a preliminary orbit before the second stage ignites to achieve the necessary velocity for orbital insertion.
The fairings will deploy, exposing the "Celestial Mapper" satellite to space as the rocket continues its ascent.
Once in the designated orbit, the satellite will be released from the rocket's payload adapter, initiating its mission to monitor Earth's environment and gather valuable data for scientific research and environmental assessment.
Mission Impact:
The "Celestial Mapper" satellite will provide valuable insights into various Earth processes, including; land use, vegetation health, atmospheric composition, and climate patterns.
Data collected by the satellite will contribute to scientific research, environmental monitoring, disaster management, and resource management efforts worldwide.
The "Cosmic Explorer" mission represents another milestone in WSA's commitment to advancing space science and fostering international collaboration in space exploration and Earth observation.
HISTORY OF SV
In the late 20th century, as space exploration gained momentum, various nations and organizations began investing heavily in aerospace technology. The West Space Agency (WSA) emerged as a key player, fueled by the collective ambition of Western nations to push the boundaries of space exploration.
The SIL Project:
In the early 21st century, WSA initiated the Spacecraft Integration and Launch (SIL) Project, aiming to develop a versatile and reliable launch vehicle capable of delivering payloads to a variety of orbits. The SIL Project was fueled by collaboration among leading aerospace companies and research institutions under WSA's umbrella.
Conceptualization and Design Phase:
The SIL Project underwent an extensive conceptualization and design phase, leveraging the expertise of WSA's engineers and partners. Drawing on decades of experience and lessons learned from previous missions, they outlined the blueprint for a modular and adaptable launch system.
Technical Breakthroughs:
Throughout the development process, the SIL Project achieved several technical breakthroughs. Advances in propulsion, materials science, and manufacturing techniques allowed for the creation of a robust and cost-effective launch vehicle. Key innovations included the development of lightweight composite materials and highly efficient rocket engines.
Testing and Validation:
Years of rigorous testing and validation followed the design phase. WSA established state-of-the-art testing facilities to evaluate the performance and reliability of the SIL launch vehicle under simulated flight conditions. Full-scale engine tests, structural tests, and integrated systems tests were conducted to ensure the vehicle's readiness for flight.
Maiden Flight:
In 2030, after extensive preparations and meticulous testing, the SIL launch vehicle, christened "Stellar Vanguard," embarked on its maiden flight. The successful launch marked a significant milestone for WSA and the SIL Project, demonstrating the vehicle's capability to deliver payloads to orbit with precision and reliability.
Operational Success:
Following the maiden flight, the "Stellar Vanguard" rocket entered commercial service, providing launch services for satellites, space probes, and scientific missions. Its versatility and reliability made it a preferred choice for governments, space agencies, and commercial entities seeking access to space.
Legacy and Impact:
The "Stellar Vanguard" rocket played a crucial role in advancing space exploration and technology. Its contributions to satellite deployment, space science, and international cooperation helped shape the future of space exploration. The SIL Project's success solidified WSA's reputation as a leader in aerospace innovation and collaboration.
Continued Evolution:
As technology continued to evolve, WSA remained committed to the continuous improvement of the "Stellar Vanguard" rocket. Updates and enhancements to the launch vehicle ensured its competitiveness in the global space launch market, enabling WSA to remain at the forefront of space exploration and commercial space activities.
EXTRA INFO
First Stage Engines:
Type:
Liquid Rocket Engines
Configuration:
Clustered arrangement of four main engines
Fuel:
Liquid oxygen (LOX) and RP-1 (Rocket Propellant-1, a refined form of kerosene)
Thrust:
Each engine produces approximately 500,000 pounds of thrust, totaling 2,000,000 pounds of thrust for the entire first stage
Propulsion System:
Gas-generator cycle
Nozzle:
Gimbaled for thrust vector control
Ignition System:
Dual redundant ignition system for reliability
Manufacturer:
Developed and manufactured by a consortium of aerospace companies under the oversight of WSA


Second Stage Engine:
Type:
Liquid Rocket Engine
Fuel:
Liquid hydrogen (LH2) and liquid oxygen (LOX)
Configuration:
Single engine mounted at the base of the second stage
Thrust:
Approximately 200,000 pounds of thrust
Specific Impulse:
450 seconds
Propulsion Cycle:
Closed-cycle, regeneratively cooled, gas-generator cycle
Nozzle:
Gimbaled for precise control of the rocket's trajectory
Ignition System:
Dual redundant ignition system for reliability
Manufacturer:
Developed and manufactured by a leading aerospace company contracted by WSA


Old Missions That Have Been Completed
Lunar Explorer Mission:
Mission Objective: Conduct lunar exploration and scientific research.
Payload: Lunar lander and rover equipped with instruments for geological analysis and surface imaging.

Mission Outcome: Successful landing and deployment of the rover on the lunar surface. The rover conducted extensive surveys and experiments, providing valuable data on lunar geology and resource potential.
Mars Orbiter Mission:
Mission Objective: Study the Martian atmosphere, surface, and climate.
Payload: Orbiter equipped with remote sensing instruments, including cameras, spectrometers, and radar for mapping and analysis.

Mission Outcome: The orbiter successfully entered Martian orbit and conducted comprehensive observations of the planet's surface features, atmospheric dynamics, and seasonal changes. Data collected contributed to our understanding of Mars' geological history and potential for past or present habitability.
Global Telecommunications Satellite Deployment:
Mission Objective: Deploy a constellation of communication satellites to provide global telecommunications coverage.
Payload: Multiple communication satellites equipped with transponders and antennas for relaying signals.

Mission Outcome: The "Stellar Vanguard" rocket successfully deployed a series of communication satellites into geostationary orbit, expanding global connectivity and supporting telecommunications networks worldwide.
International Space Station Resupply Missions:
Mission Objective: Deliver cargo and supplies to the International Space Station (ISS).
Payload: Cargo spacecraft loaded with food, water, equipment, and scientific experiments for the ISS crew.
Mission Outcome: Multiple successful resupply missions ensured the continuous operation of the ISS and supported scientific research conducted onboard by international astronauts.
Space Telescope Deployment:
Mission Objective: Deploy a space telescope for astronomical observations.
Payload: Space telescope equipped with advanced imaging sensors and spectrographs.
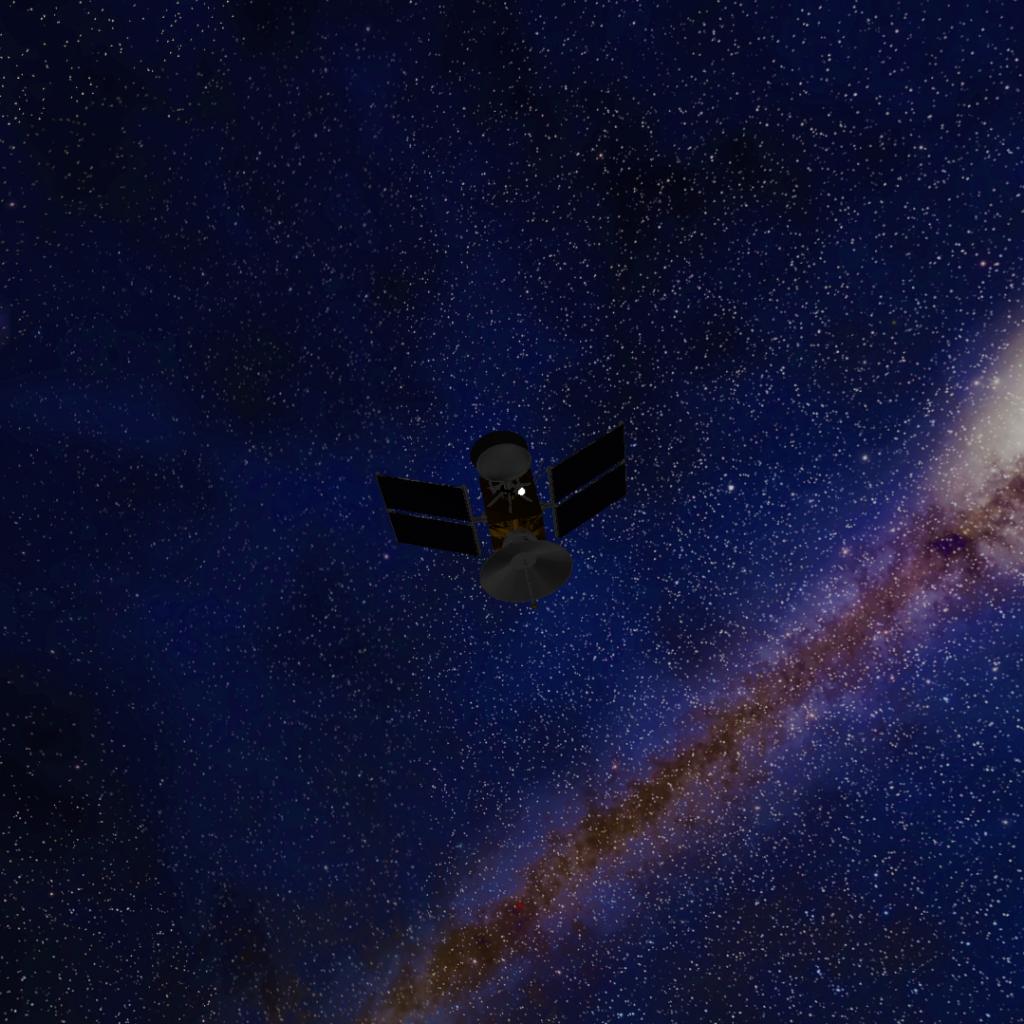

Mission Outcome: The "Stellar Vanguard" rocket successfully deployed the space telescope into orbit, enabling groundbreaking observations of distant galaxies, stars, and celestial phenomena, contributing to our understanding of the universe's origins and evolution.
More pics/videos of SV



GENERAL INFO
- Created On: Android
- Game Version: 1.3.108.0
- Price: $53,931k
- Number of Parts: 291
- Dimensions: 63 m x 7 m x 7 m
PERFORMANCE
- Total Delta V: 5.7km/s
- Total Thrust: 18.9MN
- Engines: 17
- Wet Mass: 9.66E+5kg
- Dry Mass: 79,597kg
STAGES
| Stage | Engines | Delta V | Thrust | Burn | Mass |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 4 | 3.7km/s | 15.9MN | 2.5m | 9.66E+5kg |
| 2 | 4 | 3m/s | 57kN | 16s | 2.66E+5kg |
| 3 | 1 | 2.0km/s | 2.2MN | 3.2m | 2.66E+5kg |