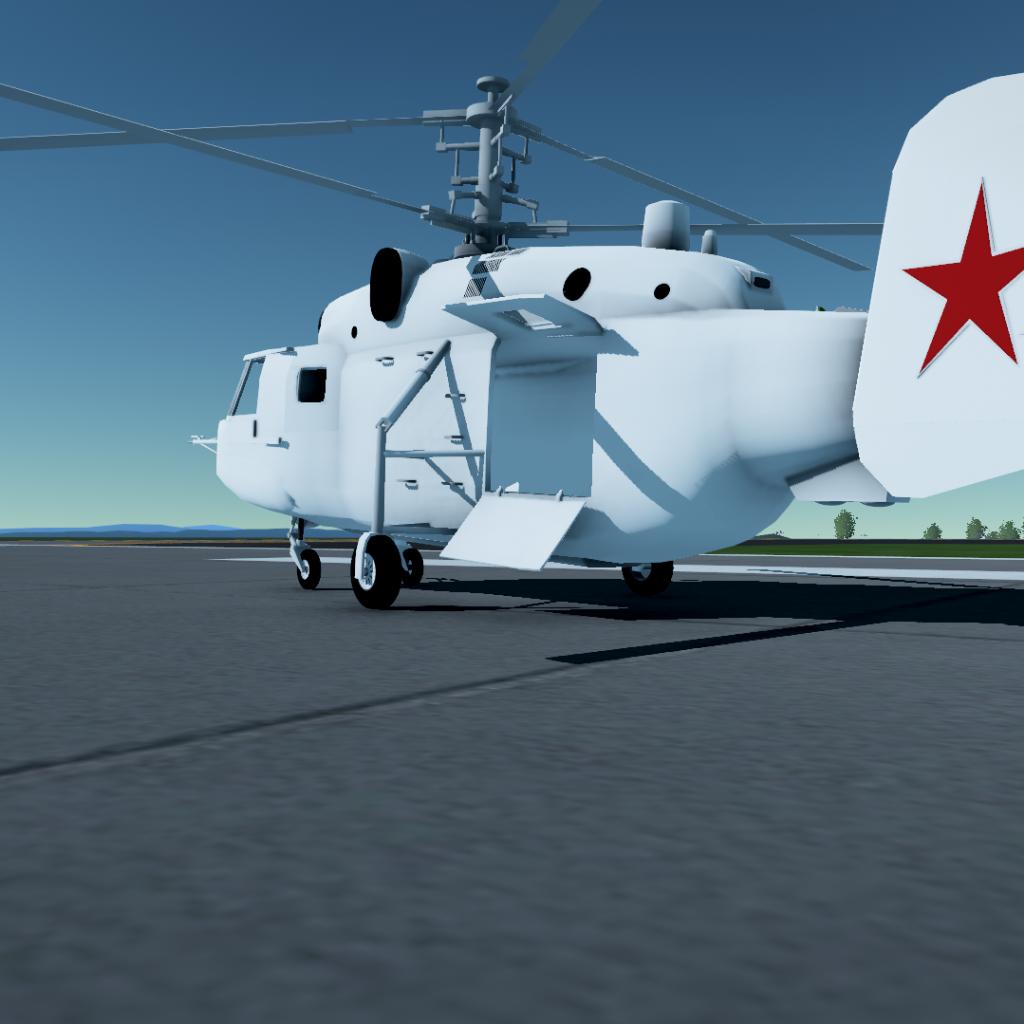
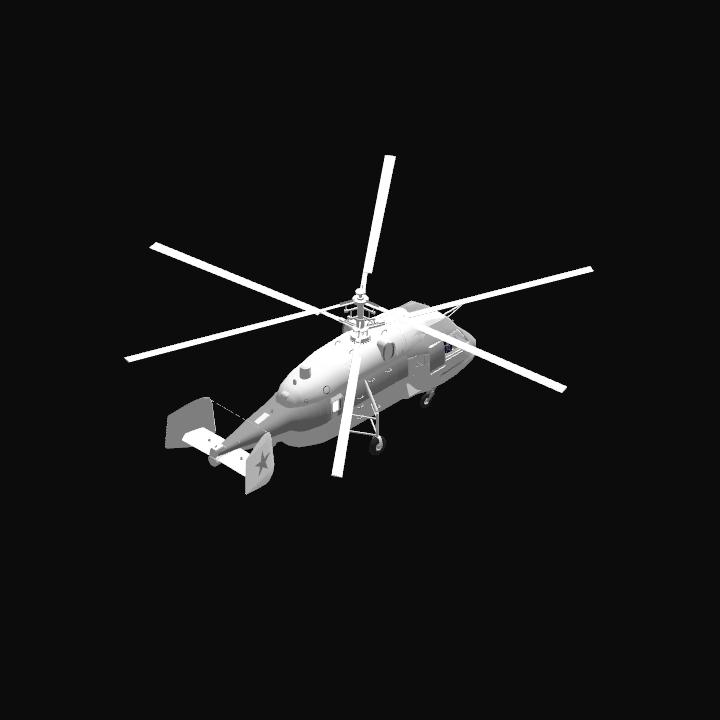
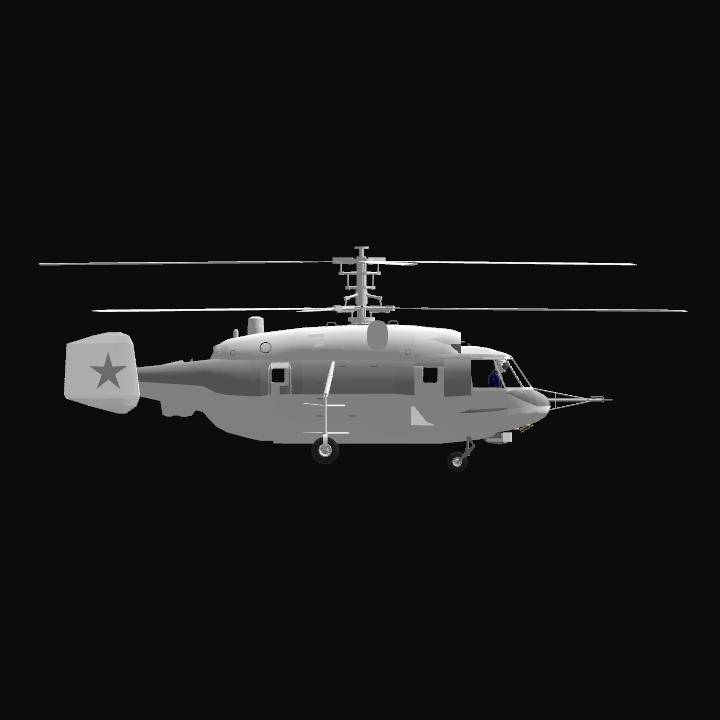
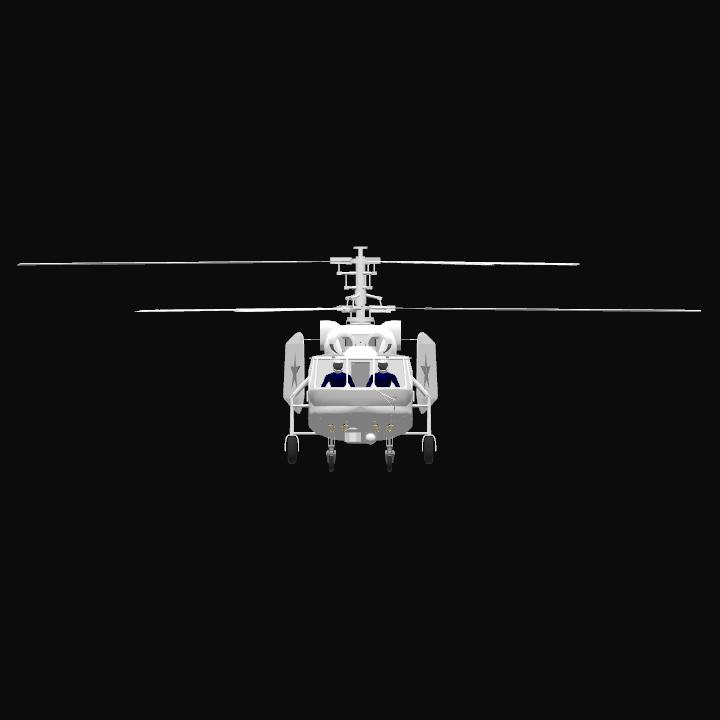
Design and development
The helicopter was developed for ferrying and anti-submarine warfare. Design work began in 1969 and the first prototype flew in 1973. It was intended to replace the decade-old Kamov Ka-25, and had to have identical or smaller external dimensions than its predecessor. Like other Kamov military helicopters it has coaxial rotors, removing the need for a tail rotor. In total, five prototypes and pre-series helicopters were built. Series production started at Kumertau in July 1979, and the new helicopter officially entered service with the Soviet Navy in April 1981.
The Ka-27 has a crew of three with a pilot and navigator both stationed in the cockpit, and a sonar operator seated behind them. It has a four-leg fixed landing gear. The Ka-27 is equipped with two lateral buoys, that can be inflated in the case of a forced landing on water.
The Ka-27PL anti-submarine version is equipped with a radar, and either a dipping sonar or a magnetic anomaly detector. It can also carry either up to 36 sonobuoys, or a torpedo, or between six and eight conventional depth charges, or a single nuclear one. Ka-27PLs generally operate in pairs as hunter-killer teams.
The Ka-27PS search and rescue helicopter can carry 12 folding seats or four stretchers in its cabin, and is equipped with a 300 kg (660 lb) winch. Its fuel capacity of 3,450 litres (910 US gal) is greater than the 2,940-litre (780 US gal) capacity of the Ka-27PL.
Ka-32 variants, e.g. the Klimov-powered Ka-32A11BC, have been certified for commercial operations throughout the world, notably in Canada and Europe. The Ka-32 has been certified for the newer Klimov VK-2500PS-02 engine





cute